Chronic lower back pain is a debilitating condition that affects millions of people worldwide. For many, the source of this pain lies in the facet joints of the spine, a crucial component in our spinal structure. Damage to these joints can lead to significant discomfort, impacting daily life and overall well-being.
Understanding the role of facet joints in spinal health is key to addressing the root cause of lower back pain. These joints facilitate movement and provide stability to the spine. When they become damaged or inflamed, injections can offer a diagnostic and therapeutic solution.
Key Takeaways
- Facet joint damage is a common cause of chronic lower back pain.
- Lumbar facet joint injections serve both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
- The procedure involves injecting local anesthetic and corticosteroid into or around the facet joints.
- Facet joint pain affects a significant portion of the population with chronic low back pain.
- Understanding the anatomy and function of facet joints is crucial for effective treatment.
- Facet joint injections can provide relief by reducing inflammation and interrupting pain signals.
Understanding Lumbar Facet Joints and Their Role in Back Pain
Understanding the anatomy and function of lumbar facet joints is vital for diagnosing and treating back pain effectively. Lumbar facet joints are synovial joints that connect the vertebrae, providing stability and facilitating movement in the spine.
Anatomy of Lumbar Facet Joints
The lumbar facet joints are formed by the articulation of the superior and inferior articular processes of adjacent vertebrae. These joints are lined with cartilage and surrounded by a synovial capsule, which contains synovial fluid that lubricates the joint. The facet joints are richly innervated with nociceptive nerve endings, making them a potential source of pain.
When examining the anatomy of lumbar facet joints, it’s essential to consider their role in spinal stability and mobility. The facet joints guide the movement of the spine, preventing excessive motion that could lead to injury or inflammation.
How Facet Joints Contribute to Chronic Back Pain
Facet joint syndrome develops when these joints become irritated, inflamed, or degenerated, often resulting in localized pain that can radiate to surrounding areas. Multiple mechanisms contribute to facet-mediated pain, including osteoarthritis, capsular stretching, synovial inflammation, and mechanical stress from poor posture or repetitive movements.
- Facet joint pain often worsens with extension or rotational movements of the spine.
- Patients frequently report increased stiffness in the morning.
- Chronic facet joint pain creates a cycle where pain leads to decreased movement, muscle weakness, and further joint deterioration.
For more information on managing facet joint pain, you can visit this resource that provides comprehensive insights into diagnosis and treatment options.
What is a Lumbar Facet Joint Injection?
A lumbar facet joint injection is a minimally invasive treatment designed to reduce inflammation and relieve pain in the facet joints of the lumbar spine. This procedure involves injecting medication directly into the facet joint to target the source of pain.
Definition and Purpose
Lumbar facet joint injections are used both diagnostically and therapeutically. Diagnostically, they help identify if the facet joint is the source of pain. Therapeutically, they provide relief by reducing inflammation and numbing the pain in the joint. The facet joint injection procedure is typically considered when other conservative treatments have failed to provide adequate relief.
Types of Facet Joint Injections
There are two primary types of facet joint injections: intra-articular facet joint injections and medial branch blocks. Intra-articular injections involve placing medication directly inside the joint capsule, while medial branch blocks target the nerves supplying the facet joints. The choice between these types depends on the patient’s condition and the physician’s assessment.
The medications used in injections typically include a combination of local anesthetics and corticosteroids. For instance, a common mixture includes 0.5% Bupivacaine and 40mg% Triamcinolone. The local anesthetic provides immediate pain relief, while the corticosteroid reduces inflammation over time.
| Component | Description | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| 23G Spinal Needle | For entering the facet joint | Precision in targeting the joint |
| 18G Needle | For aspirating drugs | Preparing the medication |
| 24G Hypodermic Needle | For skin infiltration with lignocaine | Local anesthesia |
| 1ml Insulin Syringe | For delivering the injectate into the joint | Precise delivery of medication |
| 0.5% Bupivacaine and 40mg% Triamcinolone | Local anesthetic and steroid mixture | Pain relief and inflammation reduction |
For more detailed information on lumbar facet joint injections, you can visit University of Maryland Medical System’s page on Lumbar Facet Joint.
When is a Lumbar Facet Joint Injection Recommended?
The decision to undergo a lumbar facet joint injection is typically made after other causes of pain have been ruled out. Diagnosing facet joint syndrome can be challenging due to its similarity in symptoms with other spinal conditions.
Common Indications for the Procedure
Lumbar facet joint injections are considered for patients experiencing chronic back pain that has not responded to conservative treatments. The injections serve as both diagnostic tools to identify the source of pain and therapeutic interventions to provide pain relief. Common indications include persistent pain that is suspected to originate from the facet joints, which can be due to degenerative changes, inflammation, or other factors.
Diagnostic blocks involve injecting a local anesthetic into the suspected painful facet joint. If the patient experiences significant pain relief (>50%), it confirms the joint as a pain generator. This method is particularly valuable because imaging studies often show degenerative changes in both symptomatic and asymptomatic facet joints, making clinical correlation necessary.
Diagnostic vs. Therapeutic Applications
Facet joint injections have dual purposes: diagnostic and therapeutic. For diagnostic purposes, a small amount of local anesthetic is used to confirm whether a specific facet joint is the source of pain. For therapeutic purposes, corticosteroids are added to the injection to reduce inflammation and provide longer-lasting pain relief, potentially lasting weeks to months.
Therapeutic injections may be repeated if they provide significant relief, though protocols limit the frequency to avoid complications from repeated steroid exposure. The results of diagnostic facet injections guide further treatment decisions, such as proceeding to radiofrequency ablation for longer-term relief or focusing on other potential pain generators if the blocks are not effective.
Preparing for Your Lumbar Facet Joint Injection
To ensure a smooth and successful lumbar facet joint injection, patients must follow specific preparation guidelines. Proper preparation is crucial for the safety and effectiveness of the facet joint injection procedure.
Medical Evaluation and Considerations
Before the facet joint injection, a thorough medical evaluation is necessary. This includes reviewing your medical history, current medications, and any allergies. It’s also essential to inform your healthcare provider about any new symptoms, such as fever or increased pain, which might necessitate rescheduling the procedure. For more information on aftercare, you can visit https://myhealth.alberta.ca/Health/aftercareinformation/pages/conditions.aspx?hwid=abq3934.
Medication Adjustments Before the Procedure
Patients may need to adjust their medications before the injection. This typically involves stopping blood thinners or other medications that could interfere with the procedure or increase the risk of complications. Your healthcare provider will give specific instructions on which medications to stop and when.
Day-of-Procedure Instructions
On the day of the facet joint injection, patients should follow specific instructions. This includes showering and washing the skin with regular soap, avoiding lotions or medicated creams around the area of the injection, and wearing loose, comfortable clothing. It’s also recommended to arrive at least 30 minutes early and have someone available to drive you home after the procedure.
| Preparation Task | Description |
|---|---|
| Shower and skin preparation | Wash your skin with regular soap; avoid lotions or medicated creams around the injection area. |
| Clothing | Wear loose, comfortable clothing that provides easy access to the lower back. |
| Arrival Time | Arrive at least 30 minutes before the scheduled procedure time. |

“Proper preparation is key to a successful lumbar facet joint injection.”
The Lumbar Facet Joint Injection Procedure
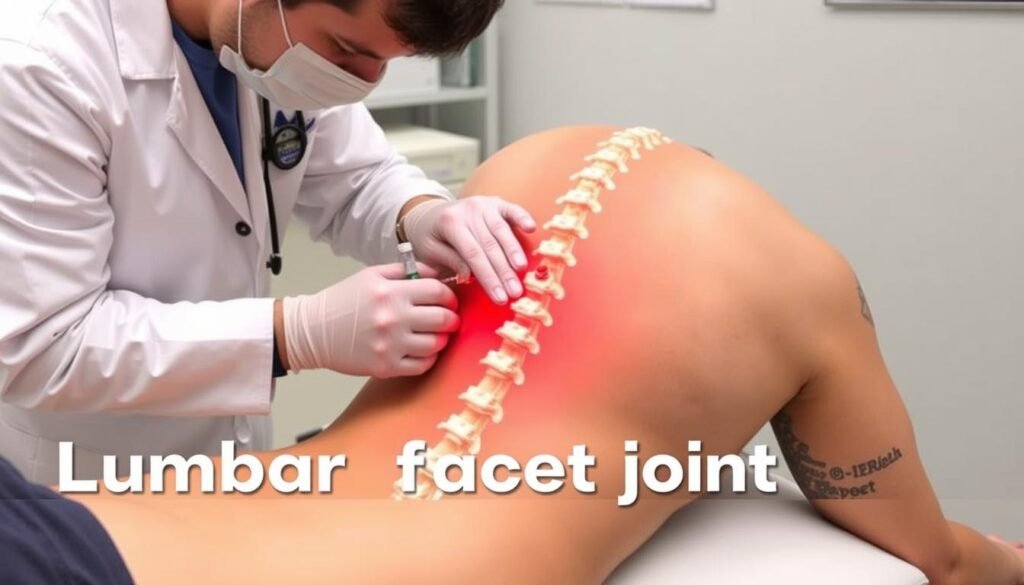
The lumbar facet joint injection is a precise procedure that requires careful preparation and execution. This medical intervention is designed to alleviate pain stemming from the facet joints in the lumbar region.
Patient Positioning and Setup
To begin, the patient is positioned on an X-ray table, typically lying on their stomach. The skin area where the injection will be administered is cleaned and prepared with an antiseptic solution to minimize the risk of infection.
Imaging Guidance Techniques
Fluoroscopic guidance is used to ensure accurate needle placement. This involves using a continuous X-ray beam to visualize the needle and guide it to the target facet joint. A contrast agent may be used to confirm the correct placement within the joint space.
Step-by-Step Injection Process
The injection process involves several key steps. First, the skin is anesthetized with a local anesthetic to reduce discomfort. A thin needle is then carefully advanced toward the targeted facet joint under fluoroscopic guidance. Once the needle is correctly positioned, a contrast agent is injected to verify the placement. Finally, a therapeutic mixture containing a corticosteroid and local anesthetic is injected into the facet joint. The needle is then removed, and the injection site is cleaned and bandaged.
The entire procedure typically takes 10-15 minutes per joint, with additional time required if multiple levels are being treated. Patients may feel temporary pressure or a brief pain similar to their usual symptoms during the procedure, which can help confirm the correct target.
What to Expect During and Immediately After the Procedure
As patients undergo a lumbar facet joint injection, it’s essential to know the sensations they might experience and the monitoring that follows. This understanding can help alleviate anxiety and improve overall outcomes.
Sensations During the Injection
During thefacet joint injection, patients may experience various sensations. Some may feel a slight pinch or stinging as the needle is inserted into thefacet jointarea. Others might notice a temporary increase inpaindue to the mechanical stimulation of the joint. However, this typically subsides within 24 to 48 hours. The injection of the local anesthetic and steroid medication can also cause a feeling of pressure or coldness in the area.
Immediate Post-Procedure Monitoring
After the injection, patients are escorted to a recoveryareawhere they are monitored for 15 to 45minutes. During this time, medical staff check vital signs, including blood pressure, heart rate, and oxygen saturation, to ensure there are no adverse reactions to theinjectionorprocedure. Some patients experience immediatepain reliefdue to the local anesthetic, confirming that thefacet jointwas a source of their pain.
| Monitoring Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Vital Signs | Blood pressure, heart rate, oxygen saturation |
| Pain Levels | Comparison of pre-procedure and post-procedure pain |
| Adverse Reactions | Checking for any complications or side effects |
Before discharge, patients receive detailed instructions on activity restrictions, potential side effects, and follow-up care. It’s recommended that patients have someone drive them home as a safety precaution.
Post-Procedure Care and Recovery
Proper care after a lumbar facet joint injection is essential for minimizing potential complications and ensuring the best possible outcome. The area around the joint may be irritated during the procedure, potentially causing temporary discomfort before the steroid takes effect.
Activity Restrictions and Recommendations
After the procedure, patients are generally advised to avoid strenuous activities for a short period. Resting the affected area can help in reducing the risk of complications. While specific activity restrictions may vary, most patients can resume their normal activities within a day or two. It’s recommended to follow the doctor’s instructions regarding post-procedure activities to ensure a smooth recovery.
- Avoid heavy lifting or bending.
- Limit strenuous activities for 24-48 hours.
- Gradually resume normal activities as comfort allows.
Managing Post-Injection Discomfort
Some degree of discomfort after a lumbar facet joint injection is common, with patients possibly experiencing temporary soreness or stiffness in the facet joint area. This discomfort can usually be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen. Applying ice to the injection site can also help reduce local inflammation and discomfort.
- Use acetaminophen for pain relief as directed.
- Avoid NSAIDs like ibuprofen for 2-3 days.
- Apply ice to the injection site for 15-20 minutes every 2-3 hours.
It’s essential to be patient, as the therapeutic effect of the steroid typically takes 2-5 days to begin, providing pain relief. If severe pain or other concerning symptoms occur, patients should contact their healthcare provider promptly.
Benefits of Lumbar Facet Joint Injections
Lumbar facet joint injections are a valuable treatment option, offering both diagnostic and therapeutic benefits. By targeting the facet joints, this procedure can provide substantial pain relief and improved function.
Pain Relief Outcomes
One of the primary benefits of lumbar facet joint injections is significant pain relief. Identifying that a facet joint injection has provided relief from pain is a necessary first step for patients who are potential candidates for radiofrequency facet joint nerve blocks. Many patients experience a notable reduction in pain following the procedure.
Improved Function and Quality of Life
Beyond pain relief, lumbar facet joint injections can significantly improve functional capacity. Patients often report enhanced mobility, improved sleep quality, and reduced reliance on pain medications. The reduction in pain breaks the cycle of inactivity and deconditioning, enabling patients to participate more effectively in rehabilitation programs and physical therapy. Improved function may include better ability to perform routine tasks and return to work activities. The overall improvement in quality of life extends beyond physical function to include social engagement and general well-being.
Potential Risks and Complications
Understanding the potential risks and complications of lumbar facet joint injections is crucial for informed decision-making. While these procedures are generally safe, being aware of the possible side effects and complications can help patients prepare and respond appropriately.
Common Side Effects
Lumbar facet joint injections can result in several common side effects, most of which are mild and temporary. These may include localized pain or discomfort at the injection site, which can usually be managed with over-the-counter pain medications. Some patients may experience temporary numbness or weakness in the affected area, but this typically resolves on its own. Additionally, there is a small risk of allergic reactions to the medications or contrast agents used during the procedure.
Other common side effects can include vasovagal reactions, characterized by a sudden drop in heart rate and blood pressure, leading to lightheadedness or fainting. These reactions are typically self-limiting and can be managed by adjusting the patient’s position.
Rare but Serious Complications
While serious complications from lumbar facet joint injections are rare, they can occur. Infection at the injection site or within the facet joint, known as septic arthritis, is a rare but serious complication that requires prompt medical attention. Symptoms of infection can include increasing pain, redness, warmth, fever, and elevated inflammatory markers. Bleeding into the joint or hematoma formation is another rare complication, more likely in patients with bleeding disorders or those taking anticoagulant medications.
Other rare but serious complications include nerve damage from direct needle trauma, which can result in persistent numbness, weakness, or pain. Additionally, repeated injections can lead to steroid-related complications such as adrenal suppression, elevated blood sugar, decreased bone density, and, in rare cases, avascular necrosis of the hip.
Conclusion: Is a Lumbar Facet Joint Injection Right for You?
After exploring the procedure, benefits, and risks of lumbar facet joint injections, it’s clear that they can be an effective treatment option for properly selected patients. Lumbar facet joint injections can provide significant relief for individuals suffering from chronic back pain related to facet joint pathology.
These injections offer a minimally invasive alternative to surgery, with significantly lower risks and recovery time. The dual diagnostic and therapeutic nature of facet injections makes them valuable tools in managing spinal pain. Patients should have realistic expectations about outcomes, understanding that while many experience significant improvement, the duration of relief varies.
A collaborative decision-making process between patient and physician is essential, weighing the potential benefits against the risks. For those who respond positively to diagnostic blocks, more long-term solutions like radiofrequency ablation may be considered. Ultimately, lumbar facet joint injections should be viewed as one component of a comprehensive pain management strategy.

