Chronic pelvic pain can be debilitating, affecting daily life and overall well-being. For those who have not found relief through conservative management approaches, a specialized interventional procedure offers hope.
The ganglion impar nerve block is a procedure that targets the ganglion impar, a collection of nerve cells that play a critical role in transmitting pain signals from the pelvic region.
By understanding how this procedure works and its potential benefits, patients can make informed decisions about their treatment options for chronic pelvic pain and explore the possibility of effective pain relief.
Key Takeaways
- The ganglion impar nerve block is a specialized procedure for alleviating chronic pelvic pain.
- It targets the ganglion impar, a critical junction for pain signals.
- This procedure is considered for patients who have not responded to conservative management.
- Understanding the procedure is crucial for patients considering this treatment option.
- Effective pain relief is a potential outcome of the ganglion impar nerve block.
Understanding the Ganglion Impar and Pelvic Pain
Understanding the ganglion impar is essential for comprehending the mechanisms behind pelvic pain. The ganglion impar is a critical nerve structure that plays a significant role in transmitting pain signals from the pelvic region to the brain.
What is the Ganglion Impar?
The ganglion impar is a solitary ganglion located at the sacrococcygeal junction, representing the most caudal (tailward) part of the sympathetic chain. It is a crucial structure where sympathetic fibers from the pelvic region converge. As noted by pain management specialists, “The ganglion impar serves as a critical relay station for nociceptive and sympathetic signals from the perineum, coccyx, and lower pelvic structures.”
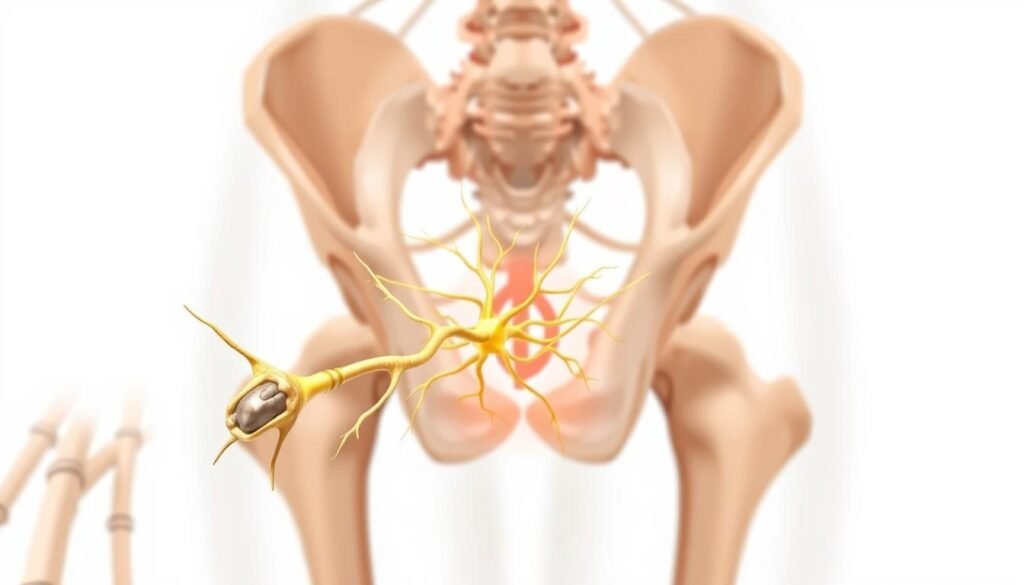
How Pelvic Pain Relates to the Ganglion Impar
Pelvic pain conditions often involve complex neural pathways that transmit pain signals through the ganglion impar to the central nervous system. When tissue damage, inflammation, or nerve irritation occurs in the pelvic region, pain signals travel via sympathetic fibers that converge at the ganglion impar. For patients suffering from chronic pelvic pain or perineal pain, targeting the ganglion impar with local anesthetics or other agents can provide significant relief. For more information on treatments like the ganglion impar nerve block, visit Ainsworth Institute.
By understanding the role of the ganglion impar in pelvic pain, healthcare providers can develop effective treatment strategies to manage chronic pain conditions. The ganglion impar nerve block is one such treatment that has shown promise in providing relief for patients with intractable pelvic pain.
Common Conditions Treated with Ganglion Impar Nerve Block
For patients suffering from specific types of pelvic pain, a ganglion impar nerve block is a viable treatment approach. This procedure is particularly useful for managing pain that originates from the lower pelvic or groin area, often caused by dysfunction or damage to organs in these regions.
Coccydynia (Tailbone Pain)
Coccydynia, or tailbone pain, is a condition that can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. A ganglion impar block can provide pain relief for individuals suffering from coccydynia by targeting the source of the pain.
Perineal Pain
Perineal pain, which occurs in the area between the genitals and anus, can be challenging to manage. The ganglion impar nerve block offers a potential treatment option for perineal pain that is resistant to other forms of management.
Cancer-Related Pelvic Pain
Cancer-related pelvic pain is a complex issue, often associated with advanced pelvic malignancies such as rectal, anal, vaginal, vulvar, prostate, or bladder cancer. Ganglion impar blocks, particularly neurolytic blocks using alcohol or phenol, can provide significant pain relief for patients with intractable malignant pain, improving their quality of life and reducing the need for opioids.
How Ganglion Impar Nerve Block Works
Ganglion impar nerve block works by interrupting pain signals sent to the brain, offering relief to patients with chronic pelvic pain. This procedure involves injecting medication into the ganglion impar, a nerve cluster located near the coccyx.
Pain Signal Interruption Mechanism
The ganglion impar nerve block procedure interrupts pain signals by injecting medication directly into or around the ganglion impar. This block stops the transmission of pain signals from the pelvic area to the brain, providing relief to patients. The injection of medication is a crucial step in this process, as it ensures that the pain signals are effectively blocked.
Types of Medications Used
Various medications are used in ganglion impar blocks, depending on the intended purpose and desired duration of effect. The choice of medication is critical in determining the outcome of the procedure. Commonly used medications include:
- Local anesthetics such as lidocaine (short-acting) or bupivacaine (long-acting) to provide immediate pain relief by temporarily blocking nerve conduction.
- Corticosteroids like methylprednisolone or triamcinolone to reduce inflammation and prolong the analgesic effect of the block.
- Neurolytic agents such as alcohol or phenol for patients with cancer-related pain or those requiring longer-lasting relief.
The volume of injectate typically ranges from 3-5 ml, with concentration and dosage carefully calculated based on the patient’s condition, weight, and medical history. By using the right medication and dosage, healthcare providers can effectively manage pelvic pain and improve the patient’s quality of life.
Benefits of Ganglion Impar Nerve Block
The ganglion impar nerve block offers numerous benefits for patients suffering from pelvic pain. This procedure is designed to provide effective pain management and improve the overall quality of life for individuals dealing with chronic pelvic issues.
Pain Relief Duration
Many people feel relief from their pain soon after the procedure. The duration of this relief can vary, lasting from a few hours to several weeks or even longer, depending on the medication used. Studies have shown that after a single ganglion impar block intervention, all four patients experienced complete pain relief.

Improved Quality of Life
Beyond pain reduction, ganglion impar blocks can significantly improve patients’ overall quality of life and functional capacity. Some of the benefits include:
- Substantial improvements in sitting tolerance, allowing patients to return to work, social activities, and daily routines.
- Dramatic improvements in sleep quality, addressing a common issue for those with chronic pelvic pain.
- Reduced reliance on analgesic medications, minimizing side effects and dependency concerns.
- Psychological benefits, including reduced anxiety and depression, and improved mood.
By providing effective pain management, ganglion impar nerve block can significantly enhance a patient’s overall well-being.
Preparing for a Ganglion Impar Nerve Block
To ensure a smooth and effective ganglion impar nerve block, patients must follow specific pre-procedure guidelines. Proper preparation is key to maximizing the therapeutic benefits of the procedure and minimizing potential complications.
Medical Evaluation and Requirements
Before the procedure, a thorough medical evaluation is necessary to assess the patient’s overall health and determine the suitability of the ganglion impar nerve block. This evaluation may include a review of the patient’s medical history, current medications, and any allergies. It’s essential to disclose all relevant medical information to your healthcare provider to ensure a safe and effective procedure.
Pre-Procedure Guidelines
Specific guidelines must be followed to ensure the success of the ganglion impar nerve block. These include:
- Fasting for 4-6 hours before the procedure if sedation is administered, although clear liquids may be permitted up to 2 hours prior.
- Temporarily discontinuing anticoagulant and antiplatelet medications according to established guidelines, with physician approval and appropriate bridging therapy if necessary.
- Arranging for transportation home after the procedure, as driving is not permitted following sedation or if there is any potential for motor or sensory changes.
- Wearing comfortable, loose-fitting clothing and removing all jewelry or metal objects that could interfere with fluoroscopic imaging on the day of the procedure.
Following these guidelines is crucial for optimizing the effectiveness of the ganglion impar nerve block and ensuring patient safety. Your healthcare provider may provide additional instructions tailored to your specific needs.
| Pre-Procedure Guidelines | Description |
|---|---|
| Fasting | 4-6 hours before the procedure (clear liquids up to 2 hours prior if sedation is used) |
| Medication Management | Temporarily discontinue anticoagulant and antiplatelet medications as directed |
| Transportation | Arrange for someone to drive you home after the procedure |
| Clothing and Jewelry | Wear loose-fitting clothing and remove jewelry or metal objects |
The Ganglion Impar Nerve Block Procedure
To administer a ganglion impar nerve block, healthcare providers use a specialized technique that involves injecting medication into a specific area. The procedure is typically performed in a procedure room equipped with fluoroscopy or other imaging modalities.
Different Approach Techniques
The ganglion impar nerve block can be performed using various approaches, each with its own advantages.
Trans-Sacrococcygeal Approach
The trans-sacrococcygeal approach involves advancing the needle through the sacrococcygeal junction to reach the ganglion impar.
Needle-Inside-Needle Technique
The needle-inside-needle technique is a specialized method that involves using a smaller needle inside a larger one to improve precision.
Paracoccygeal and Intracoccygeal Approaches
Other approaches, such as the paracoccygeal and intracoccygeal methods, may also be used depending on the patient’s anatomy and the healthcare provider’s preference.
What to Expect During the Procedure
During the procedure, the patient lies on their stomach on a procedure table and may receive sedation to help relax. The healthcare provider will clean and numb the area around the injection site before inserting the needle.
The procedure typically takes 15-30 minutes, during which the patient’s vital signs are closely monitored. Fluoroscopy or other imaging modalities are used to guide the needle to the correct position.
Risks and Potential Complications
As with any invasive medical procedure, the Ganglion Impar nerve block carries certain risks and potential complications. It’s essential for patients to be aware of these risks to make informed decisions about their care.
Common Side Effects
Common side effects of the Ganglion Impar nerve block procedure may include temporary discomfort, swelling, or bruising at the injection site. These effects are typically mild and resolve on their own within a few days.
Rare Complications
Rare but serious complications can occur, including infection, bleeding, and damage to surrounding tissue or organs. The risk of these complications can be minimized with proper technique and patient selection.
| Complication | Description | Prevention/Management |
|---|---|---|
| Infection | Risk of introducing bacteria during the procedure | Strict aseptic technique, antibiotics if necessary |
| Bleeding | Risk of bleeding due to vascular injury | Proper patient selection, careful needle placement |
| Tissue Damage | Risk of damaging surrounding structures | Imaging guidance, precise needle placement |
Recovery and Post-Procedure Care
Understanding the recovery and post-procedure care for a ganglion impar nerve block is essential for patients to achieve optimal pain relief. After the procedure, it’s crucial to follow the guidelines provided by your healthcare provider to ensure a smooth and effective recovery.
Immediate Post-Procedure Period
In the immediate post-procedure period, patients should be aware of potential side effects and complications. Your healthcare provider will give you specific instructions on what to expect and how to manage any discomfort. It’s essential to monitor your condition closely and seek medical attention if you experience severe pain, weakness or numbness in the legs, changes in bowel or bladder function, fever, bleeding at the injection site, or signs of infection such as redness, swelling, and oozing.
Long-term Follow-up
Long-term follow-up after a ganglion impar block is crucial for evaluating the treatment’s efficacy, monitoring for delayed complications, and adjusting the overall pain management plan. Most pain management specialists schedule a follow-up appointment 2-4 weeks after the procedure to assess pain levels, functional improvement, and determine if additional interventions are needed.
- Maintaining a pain diary is recommended to document pain levels, activities that aggravate or relieve symptoms, and any changes in medication requirements.
- For patients who experience significant but temporary relief, repeat blocks may be scheduled at 3-6 month intervals, with some eventually requiring only annual maintenance procedures.
- Comprehensive long-term management often incorporates physical therapy, ergonomic modifications, and behavioral strategies to maximize and prolong the benefits of the ganglion impar block.
By adhering to the post-procedure care instructions and attending scheduled follow-up appointments, patients can optimize their pain relief and improve their quality of life after undergoing a ganglion impar nerve block procedure.
Conclusion: Is Ganglion Impar Nerve Block Right for You?
The ganglion impar nerve block has emerged as a significant treatment option for individuals suffering from pelvic pain that hasn’t responded to other treatments. This minimally invasive procedure has shown considerable efficacy in providing pain relief for conditions such as coccydynia and perineal pain.
For patients who have failed conservative management, this block can be particularly beneficial. It’s crucial for patients to collaborate with their healthcare providers to determine if this treatment is suitable, considering both the potential benefits and risks. Ideal candidates are those with pain consistent with sympathetically mediated mechanisms and without contraindications.
While not a cure for the underlying pathology, the ganglion impar block can offer substantial pain relief and improve quality of life. It serves as a vital component of a comprehensive pain management strategy, which may include physical therapy, medications, and lifestyle modifications.

